Bloom’s Taxonomy
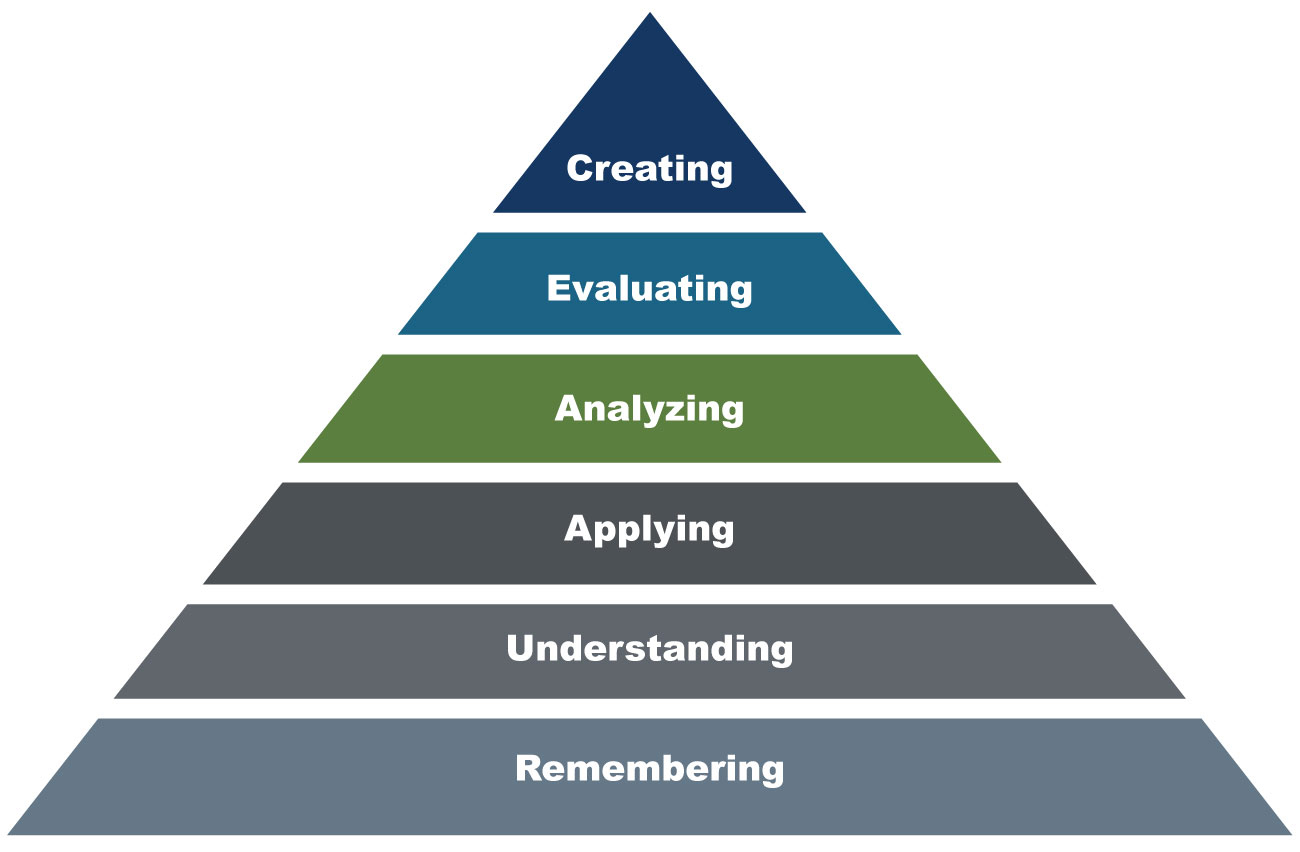
Bloom’s Taxonomy organizes learning outcomes (action verbs) into levels according to their cognitive complexity. Figure 2 shows the six levels in the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy:
- At the remembering level, participants can remember or recall previously learned information.
- At the understanding level, participants can demonstrate their understanding by explaining ideas or concepts.
- At the applying level, participants can use the new information in another familiar situation.
- At the analyzing level, participants can break information into parts to see how the parts relate to one another and to the overall conceptual structure.
- At the evaluating level, participants can make judgements using criteria and standards and can justify a decision or course or action.
- At the highest level, participants can create new ideas, products, or ways of viewing things by reorganizing information into new patterns or structures.
Use Bloom’s Taxonomy to see how lower-level thinking skills are used to support higher-level skills later in the course. Bloom’s Taxonomy can be used as a guide to selecting appropriate instructional strategies and aligning the questions and activities with the learning outcomes.